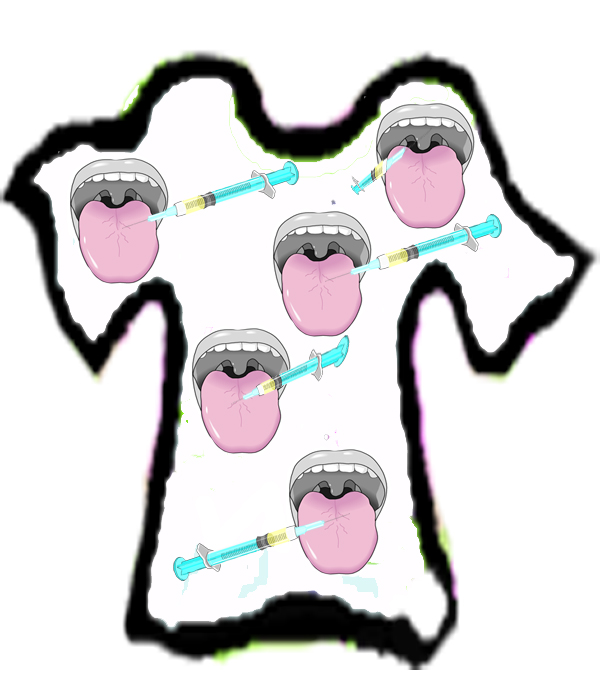
Italian pegwords
Find out about the pegword mnemonic
Here are pegwords I've thought up in the Italian language.
As with the original example, let's try it out with our cranial nerves.
In italiano, sono i nervi cranici:
- olfattorio
- ottico
- oculumotore
- trocleare
- trigemino
- abducente
- faciale
- cocleare
- glossofaríngeo
- vago
- accessorio
- ipoglosso
Each mnemonic image contains the pegword image plus something to denote the cranial nerve. In some cases, that can be very simple. But if the name of the nerve is less obvious, there will be items that refer to the function of the nerve and ones that provide keywords to the name. Such keywords are written in bold.
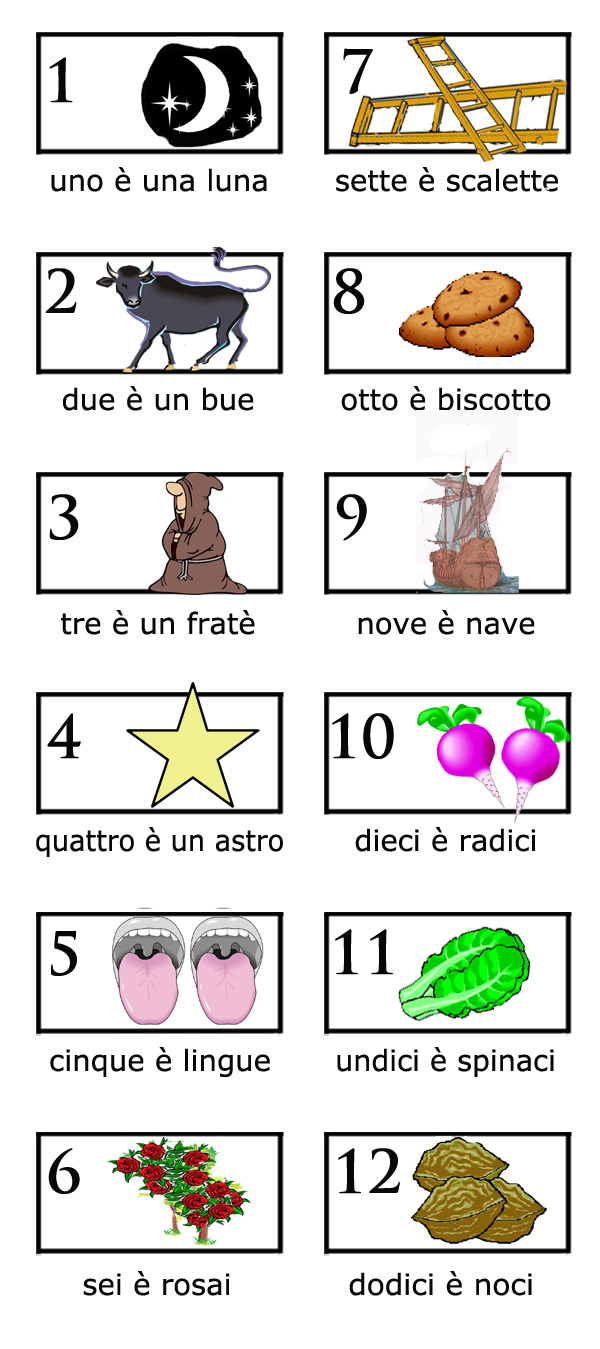
1 è la luna e il nervo cranico 1 è olfattivo - la luna con un grande naso:
1 is the moon and cranial nerve 1 is olfactory — the moon with a big nose:

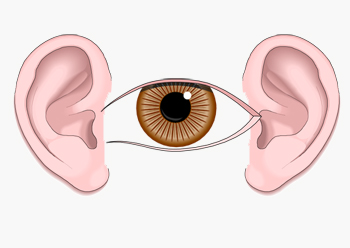
2 è un bue e il nervo cranico 2 è ottico - il bue usa una lente d'ingrandimento per leggere il giornale:
2 is an ox and cranial nerve 2 is optic — the ox uses a magnifying glass to read the newspaper:

3 è un fratè e il nervo cranico 3 è oculomotore - grandi occhiali sul motociclista che viene fermato bruscamente dai poteri del fratè:
3 is a friar and cranial nerve 3 is oculomotor — big goggles on the motorcyclist who is abruptly halted by the powers of the friar:

4 è una stella e il nervo cranico 4 è trocleare - la punta acuminata della stella penetra l'occhio ma il tricolore asciuga il sangue:
4 is a star and cranial nerve 4 is trochlear — the sharp point of the star pierces the eye but the tricolore wipes up the blood:

5 è lingue e il nervo cranico 5 è trigemino - relativo alla mascella, quindi abbiamo due lingue nella mascella e tre gemme che cadono sulla lingua distesa:
5 is tongues and cranial nerve 5 is trigeminal — relating to the jaw, so we have two tongues in the jaw and three gems falling onto the outstretched tongue:
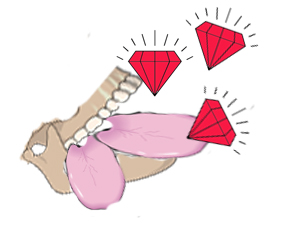
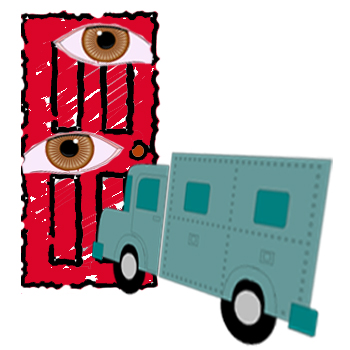
6 è rosai e il nervo cranico 6 è abducente - anche in relazione con l'occhio, quindi abbiamo rose che galleggiano sul succo di albicocca e qualcuno che raggiunge per far cadere un occhio nel bicchiere:
6 is rosebushes and cranial nerve 6 is abducens — also relating to the eye, so we have roses floating on the apricot juice and someone reaching to drop an eye in the glass:
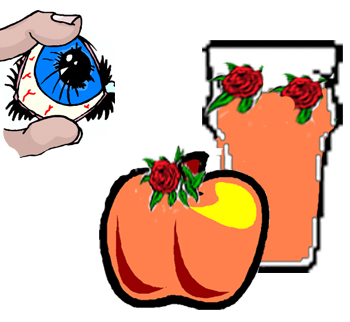
7 è scalette e il nervo cranico 7 è facciale - una scala che corre fino alla bocca su una faccina sorridente:
7 is ladders and cranial nerve 7 is facial — a ladder running up to the mouth on a smiley face:

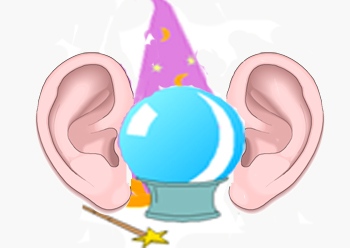
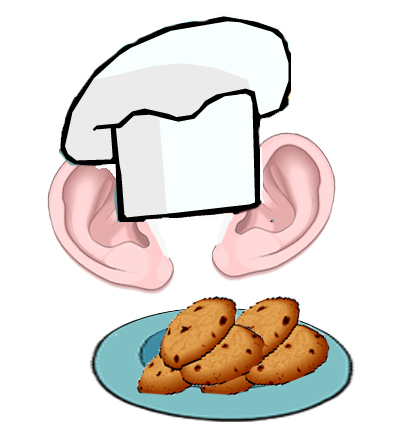
8 è biscotti e il nervo cranico è uditivo - un cappello da cuoco tra due orecchie mentre presenta i suoi biscotti:
8 is biscuits and cranial nerve is auditory — a cook's hat between two ears as he presents his biscuits:

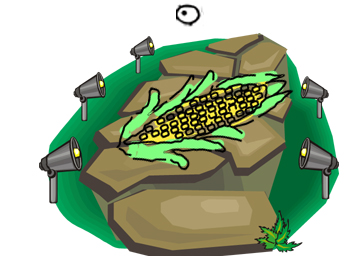
9 è nave e il nervo cranico 9 è glossofaringeo - relativo alla gola, quindi ecco un uomo che sta per ingoiare la nave con il rosmarino:
9 is a ship and cranial nerve 9 is glossopharyngeal — relating to the throat, so here is a man about to swallow the ship with rosemary:

10 è radici e il nervo cranico 10 è il vago - relativo al cuore, quindi una forma del cuore vaga rispecchiata dalla forma fatta dai due radici:
10 is radishes and cranial nerve 10 is vagus — relating to the heart, so a vague heart shape mirrored by the shape made by the two radishes:

11 è spinaci e il nervo cranico 11 è accessorio - relativo al movimento della testa, quindi abbiamo una donna che scuote la testa mentre mette gli spinaci nella sua borsa (un accessorio):
11 is spinach and cranial nerve 11 is accessory — relating to head movement, so we have a woman shaking her head as she puts spinach in her bag:

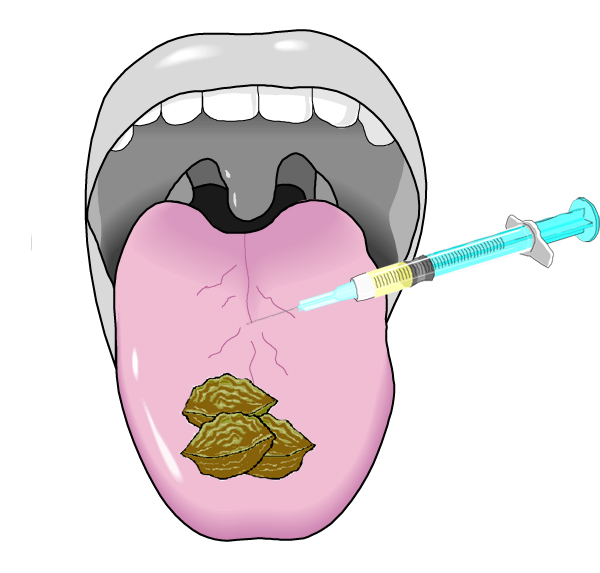
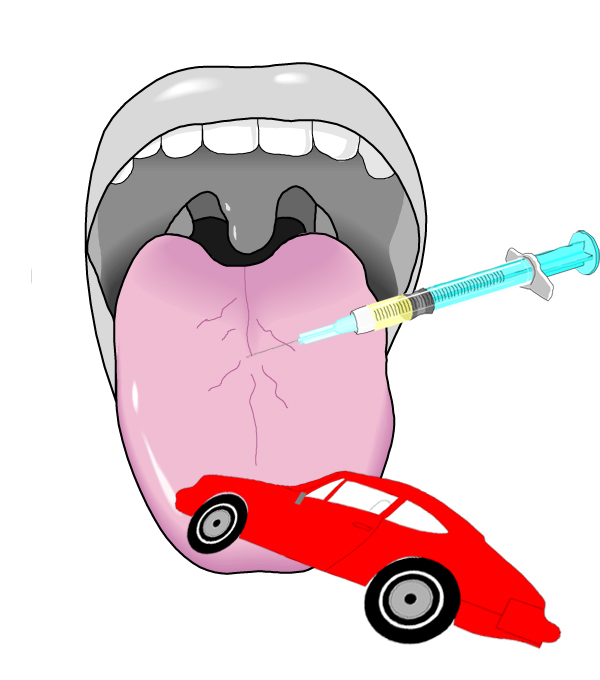
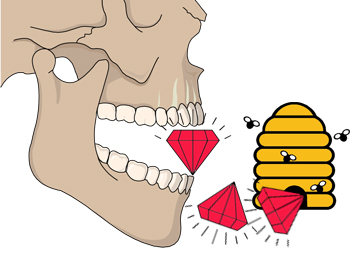
12 è noci e il nervo cranico 12 è ipoglosso - relativo alla lingua, quindi un ipodermico che inietta la lingua mentre cerca di ingoiare le noci nei loro gusci:
12 is walnuts and cranial nerve 12 is hypoglossal — relating to the tongue, so a hypodermic injecting the tongue as it tries to swallow walnuts in their shells: